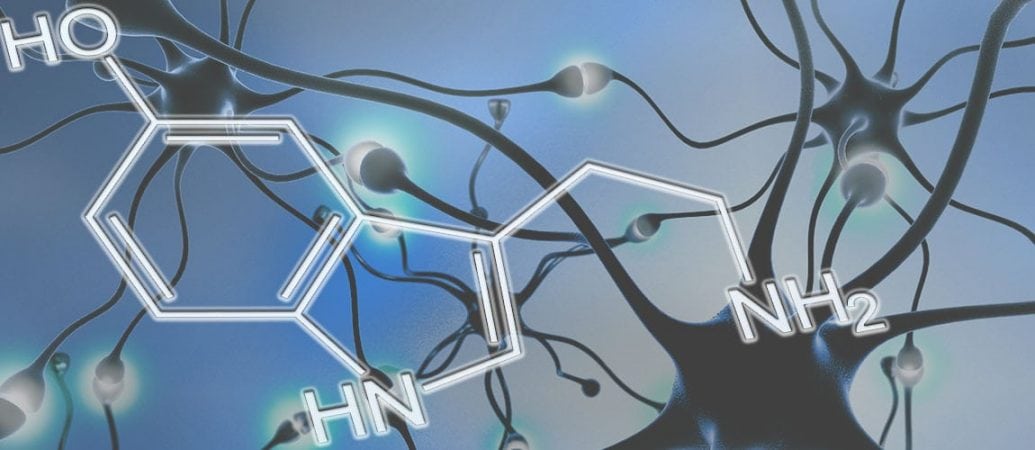
How Tryptophan Deficiency Affects Mood, Memory and More
Many people primarily associate tryptophan with the feeling of fatigue that you may feel after indulging in a Thanksgiving Day turkey feast. The truth is that although tryptophan is responsible for the release of the sleep hormone melatonin, simply eating turkey would not provide enough tryptophan to make you feel tired. In fact, there is actually less tryptophan in turkey than in other types of commonly consumed foods such as chicken. Although tryptophan can be found in a variety of foods, it is still possible to be deficient in this important compound, and a tryptophan deficiency could be the cause of some of the most nagging health and wellness issues.
Here is what you need to know about tryptophan, why it is important for overall health and wellness and how you can ensure adequate intake.
What is Tryptophan and How is Related to Serotonin?
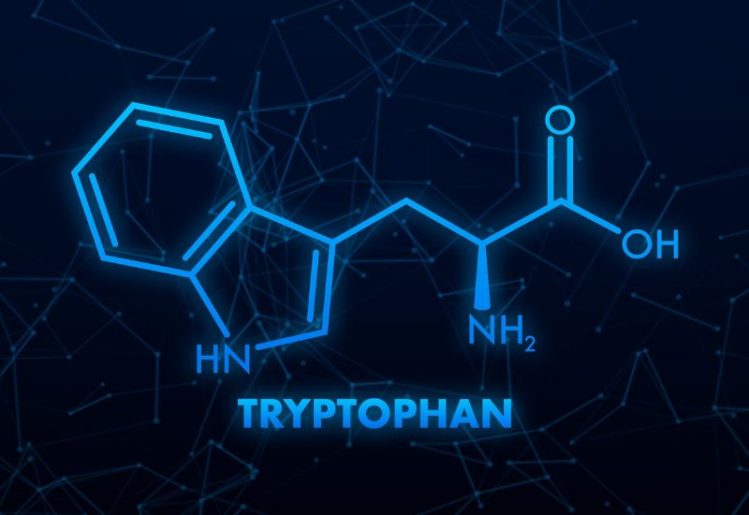 Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is instrumental in a number of different health functions. It is defined as an essential nutrient because the body is not able to produce it on its own, making it necessary that you consume it through food or supplementation. A lack of tryptophan in the diet can trigger a variety of conditions and impact health in a number of ways.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is instrumental in a number of different health functions. It is defined as an essential nutrient because the body is not able to produce it on its own, making it necessary that you consume it through food or supplementation. A lack of tryptophan in the diet can trigger a variety of conditions and impact health in a number of ways.
The primary importance of tryptophan lies in how it is used by the body to produce serotonin, the neurotransmitter that controls mood, sleep cycles and more. Tryptophan travels through the body's bloodstream to the brain where it is converted into serotonin. This serotonin then resides in the brain's neurons until it is told to be released.
Serotonin triggers a calming response when the body feels stress. You are more likely to feel happy and at peace when serotonin is released. The presence of serotonin has also been connected to a reduction in appetite, an important factor for those looking to control their weight.
Without proper intake of tryptophan, it is easy to see how the body can develop a lack of serotonin. This translates to a number of health complications, both physical and mental. For instance, you are more likely to become stressed and depressed without proper levels of serotonin. Inadequate serotonin levels have also been linked to an increase in food cravings and a harder time focusing.
Signs and Symptoms of Tryptophan Deficiency
Most people in Western countries are able to get enough tryptophan in their diets through food and supplements. However, there are a number of signs and symptoms of tryptophan deficiency that have been identified by health experts.
Some of the most likely issues that can be blamed on a tryptophan deficiency include physical symptoms such as diarrhea, a decrease in appetite or various other digestive issues. Those individuals not consuming enough tryptophan may also experience sleep issues such as insomnia. Additionally, at least one study linked tryptophan depletion to an increase in PMS symptoms.
There are also serious mental and emotional issues that have been correlated to a deficiency in tryptophan. Some of these symptoms include depression, anxiety, memory decline, onset of manic symptoms and more. Individuals suffering from bulimia nervosa have often been shown to lack serotonin, a natural byproduct of tryptophan consumption.
While this is an extreme reaction, one study even demonstrated tryptophan depletion was associated with greater levels of aggressive tendencies and hostile behavior.
Factors That Hinder Adequate Tryptophan Intake
A poor diet is the leading cause of inadequate tryptophan intake, especially in individuals who eat a limited amount of protein sources. It is also important to note that you need to be taking in enough vitamin B6, vitamin B2 and iron to support tryptophan absorption.
Too much sugar in your diet may also hinder the ability of the body to convert tryptophan to serotonin. Other factors that may hinder this intake and conversion include smoking cigarettes, too much alcohol consumption and health conditions such as diabetes and hypoglycemia. Because of the complex relationship between all of these factors, it is important to be aware of how a deficiency in one nutrient can impact the body's ability to produce what it needs for optimal health.
How to Boost Tryptophan Intake
 The good news is that tryptophan is found in a number of foods, making it easier to consume than some of the other essential nutrients. Rich sources of tryptophan include turkey, chicken, eggs, fish, cheese, milk, tofu, oats, bananas, soy products and peanuts.
The good news is that tryptophan is found in a number of foods, making it easier to consume than some of the other essential nutrients. Rich sources of tryptophan include turkey, chicken, eggs, fish, cheese, milk, tofu, oats, bananas, soy products and peanuts.
You can also boost your tryptophan intake through the use of supplements. A supplement containing tryptophan may be particularly important for vegans or vegetarians since the essential acid is most commonly found in protein sources which may be lacking in their diets. A supplement such as Serochron is uniquely formulated to support the body's ability to maintain optimal serotonin levels. This supplement is a rich source of tryptophan, niacin and vitamin B6. The supplement has been able to lean on emerging research that points to the natural short life of 5-HTP and tryptophan to provide long-lasting results through its slow-release formula.
So go ahead and feast on that delicious Thanksgiving turkey this year. Although it probably won't make you tired, the tryptophan and the resulting serotonin will do your body and your mind good.