Are Stress and Autoimmune Disease Linked by Gut Bacteria?
Each of us has a community of microorganisms that thrive in an area of our large intestines known as the gut microbiome. This part of the gut serves as a home to trillions of bacteria and other microbes that interact with the rest of the body. While some bacteria are harmful and contributes to the development of disease and infection, other types of bacteria are actually beneficial. New research finds gut bacteria play a role in the relationship between stress and autoimmune disease, suggesting a healthier lifestyle may reduce risks.
The Gut Microbiome Plays an Important Role in Overall Health
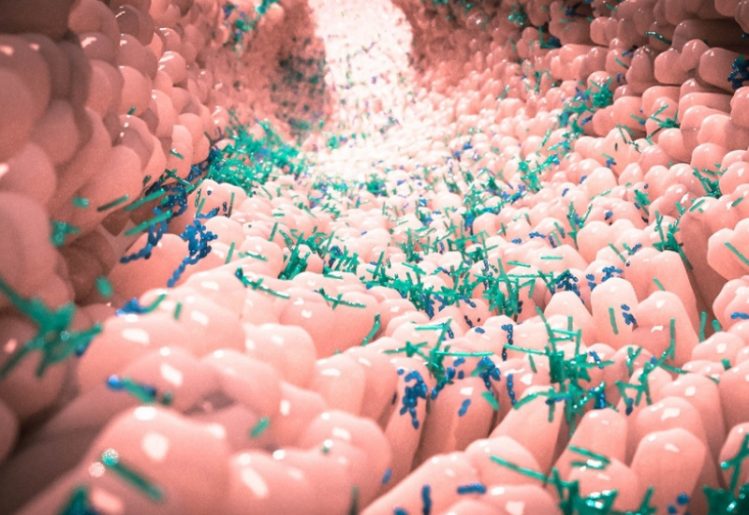 In a normal, healthy gut microbiome, there up to 1,000 different types of bacteria. This is important, because each strain serves a different function, affecting health in a unique way. For instance, Bifidobacteria is a type of bacteria that helps infants digest the sugars that are present in breast milk. Similarly, other types of bacteria help the body digest fiber more efficiently. Once digested the compounds in fiber help the body protect against heart disease, cancer and obesity.
In a normal, healthy gut microbiome, there up to 1,000 different types of bacteria. This is important, because each strain serves a different function, affecting health in a unique way. For instance, Bifidobacteria is a type of bacteria that helps infants digest the sugars that are present in breast milk. Similarly, other types of bacteria help the body digest fiber more efficiently. Once digested the compounds in fiber help the body protect against heart disease, cancer and obesity.
Research in recent years has found that the beneficial bacteria in the gut can strengthen the immune system and reduce the risks of a variety of medical conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and gastrointestinal disorders. Since the gut microbiome serves so many functions, it's now considered to be an extra organ in the body, and continuing research is finding that it benefits health in more ways than previously known.
Stress and Autoimmune Disease Linked to Gut Microbiome
While there are several illnesses that can be categorized as autoimmune diseases, all of these develop as the result of a similar process. Essentially, the immune system erroneously identifies a group of cells, an organ or some other tissue in the body as a harmful bacteria or virus. This causes the immune system to turn on the body and attack healthy tissue. Some examples of these types of illnesses include rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes and lupus.
A study conducted at Israel's Bar Ilan University found that there was a link between stress and autoimmune disease, which may involve microbial activity in the gut. Working with mice, they found that social stress caused an increase in the production of effector T helper cells. These cells are responsible for the immune system's response to threats, indicating that stress may play a role in instigating autoimmune diseases.
The researchers also found an increase of two specific types of bacteria in the gut microbiomes of the mice. These bacteria, Bilophila and Dehalobacterium, are also found in higher amounts in the gut microbiomes of people with multiple sclerosis. The increase of these types of bacteria may have something to do with the alterations of genes in the gut which occur as a result of stress. The changes to the genes in the gut help bacteria travel to other parts of the body, thrive and grow, and relay signals to various organs in the body.
As a result of the genetic changes, the bacteria travel to the lymph nodes, where they can manipulate immune responses. Essentially, stress promotes changes to the genes in the gut, which, in turn, results in changes to the how the lymph nodes manage immune responses.
This increases the risk that an individual suffering from excess stress will ultimately develop autoimmune diseases. The opposite may also be true, suggesting that managing stress can help you keep your risk of autoimmune disorders low.
Tips for Managing Stress
Exercise
Physical activity is essential to your physical health, but it also has positive effects on your mind and emotions. By working out for a minimum of 30 minutes per day, you'll experience a release of endorphins that will boost your mood and reduce stress hormones.
Reduce Substance Use
You may think that alcohol and drugs are making you feel better, but they're actually exacerbating the problem. Once that euphoric feeling wears off, stressful feelings will return. This will prompt you to take more drugs or drink more alcohol. In addition to running the risk of developing an addiction, this cycle will cause you to feel more stressed over time.
Eat a Healthy Diet
The foods you eat will also impact your emotional health. Natural foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, contain essential nutrients and vitamins that help your body and brain function. When your diet consists primarily of processed foods, you're depriving your body of these nutrients. As a result, your brain won't function as efficiently as it should, which can result in a more concentrated release of stress hormones.
Manage Time More Efficiently
 For many people, stress is increased by a lack of time to get everything accomplished. Even though you may have a lot on your plate, you can get through each day more easily by planning ahead. Just before bedtime each night, make a list of everything you need to get done on the following day and assign a block of time for each task. This will help to ensure you get everything done without feeling overly burdened.
For many people, stress is increased by a lack of time to get everything accomplished. Even though you may have a lot on your plate, you can get through each day more easily by planning ahead. Just before bedtime each night, make a list of everything you need to get done on the following day and assign a block of time for each task. This will help to ensure you get everything done without feeling overly burdened.
Relax
Each day, you should set aside some time to do something that relaxes you. Whether that's meditating and practicing yoga, reading a good book or listening to your favorite podcast, you can choose any activity you enjoy. In addition to reducing stress levels and helping you stay healthy, taking this time to unwind will also help you sleep better.





